Yangshuo 1
Submitted by qperceval on Mon, 09/10/2012 - 21:25
|
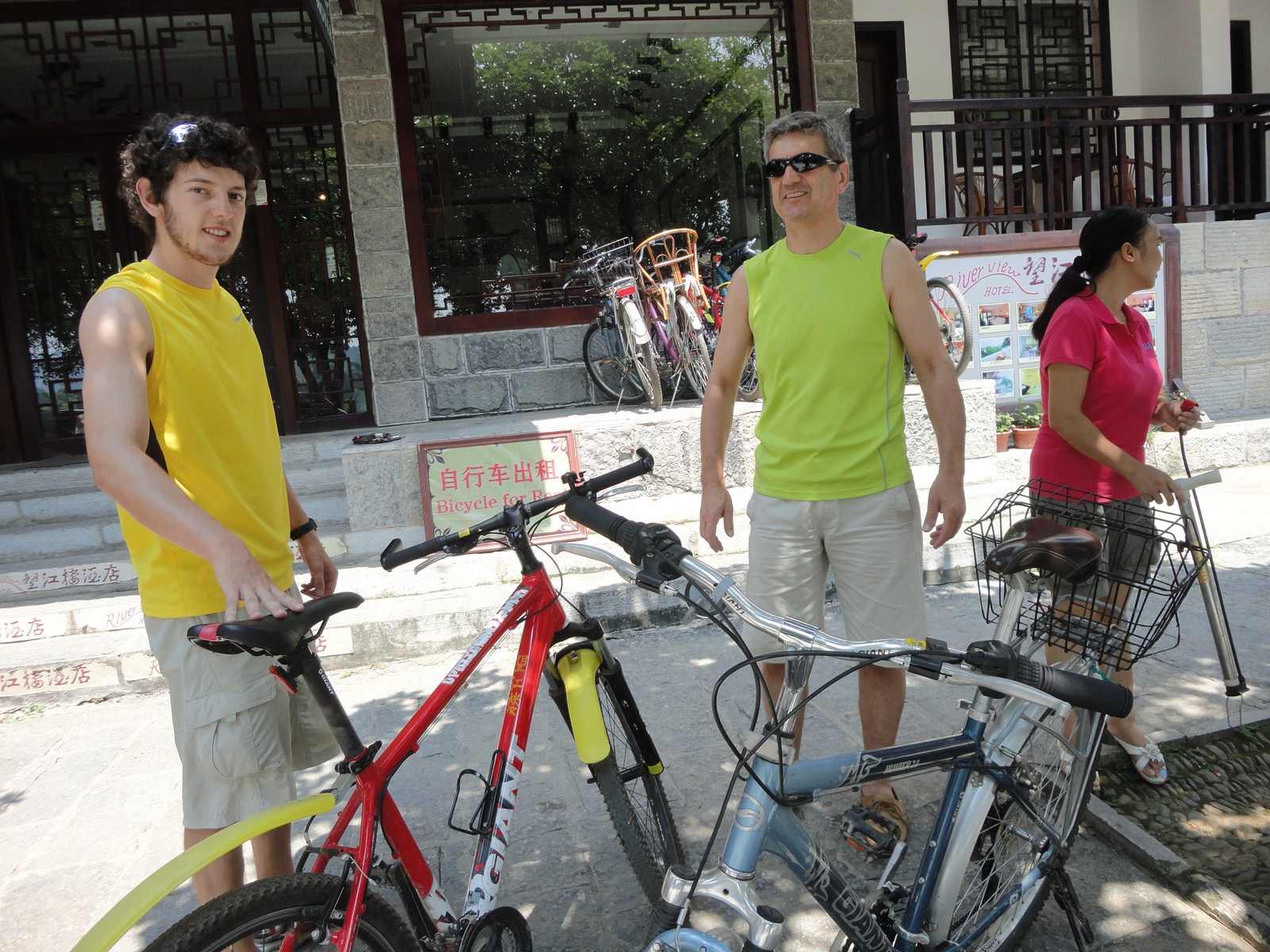
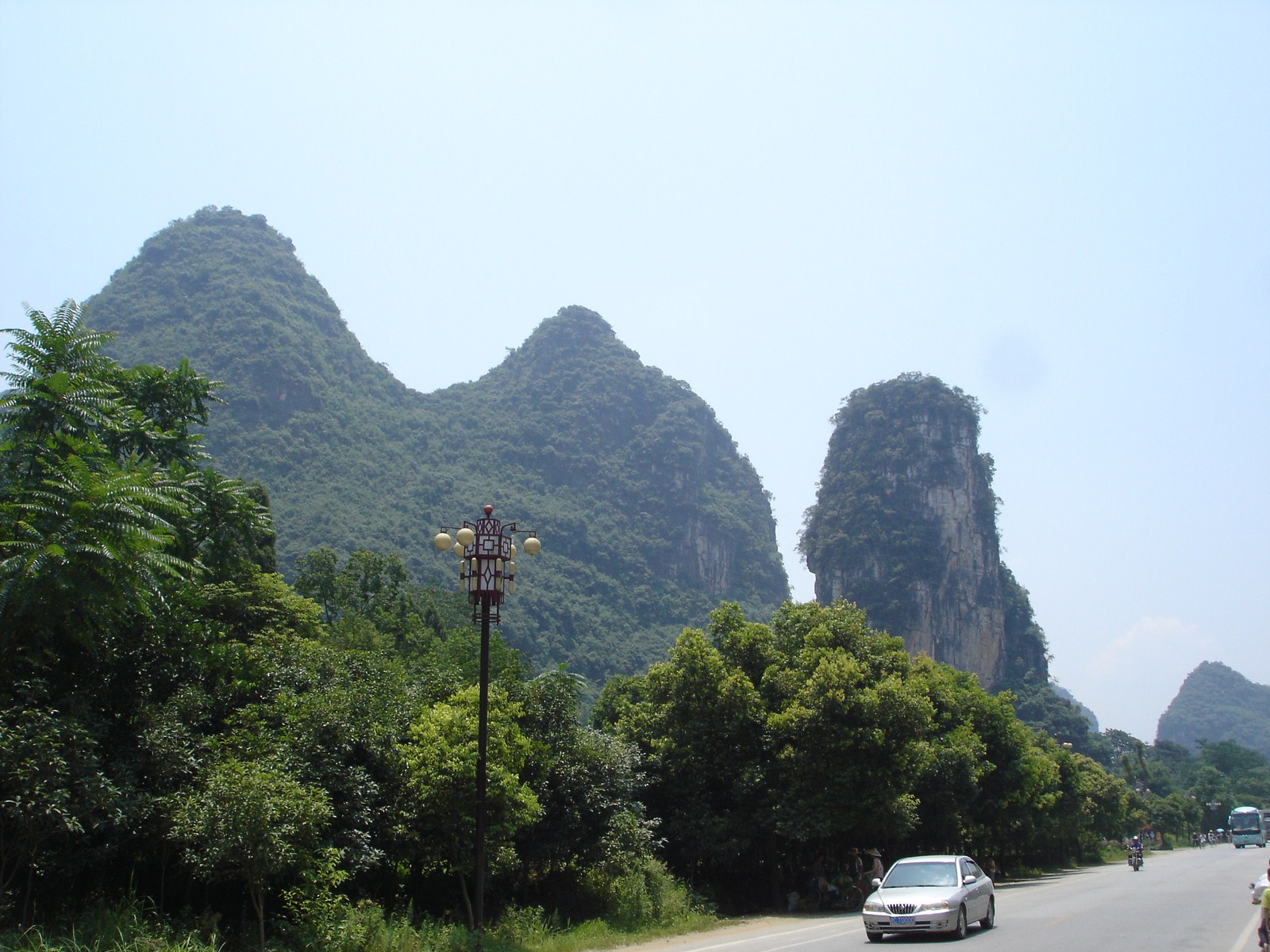
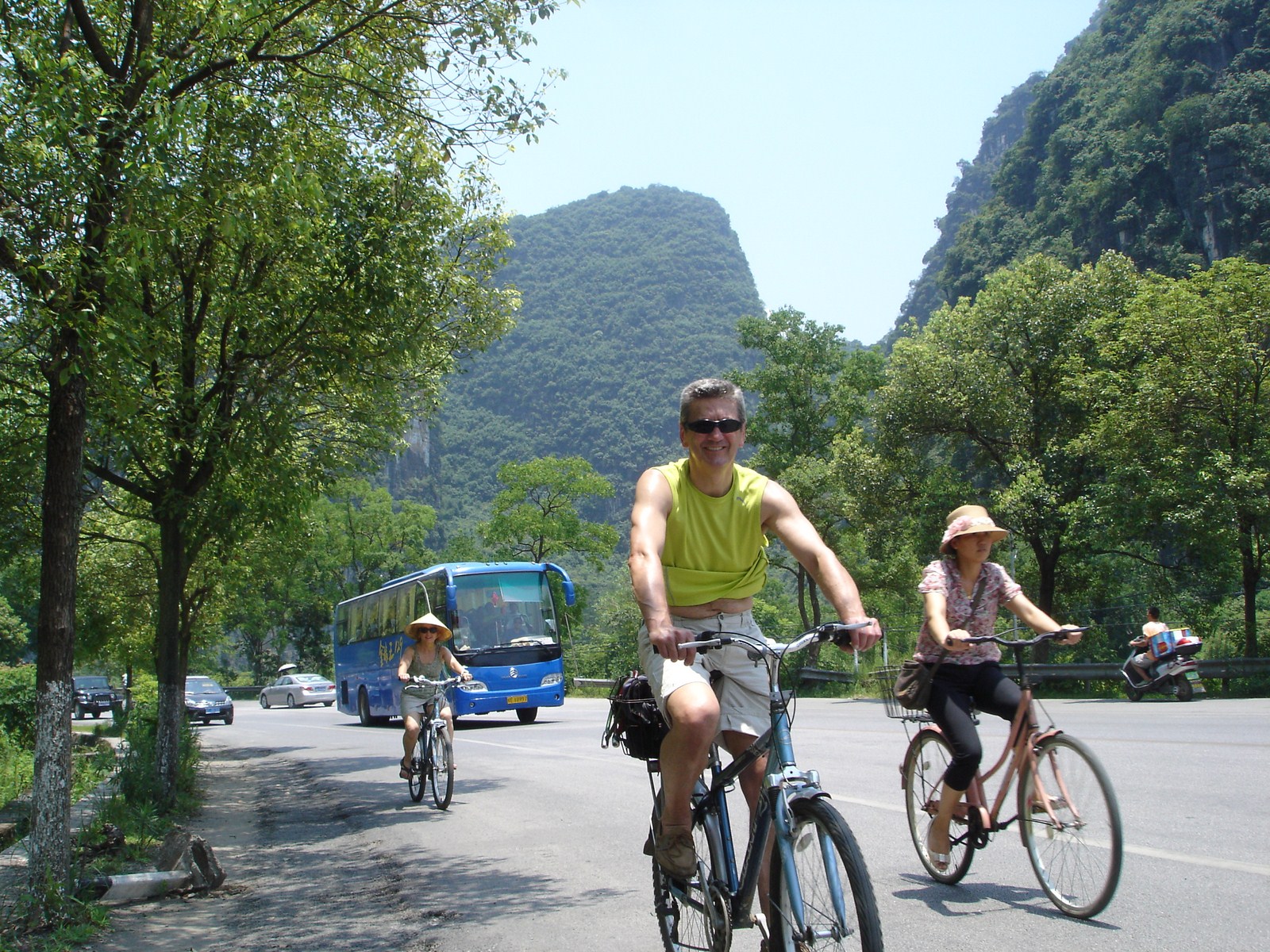
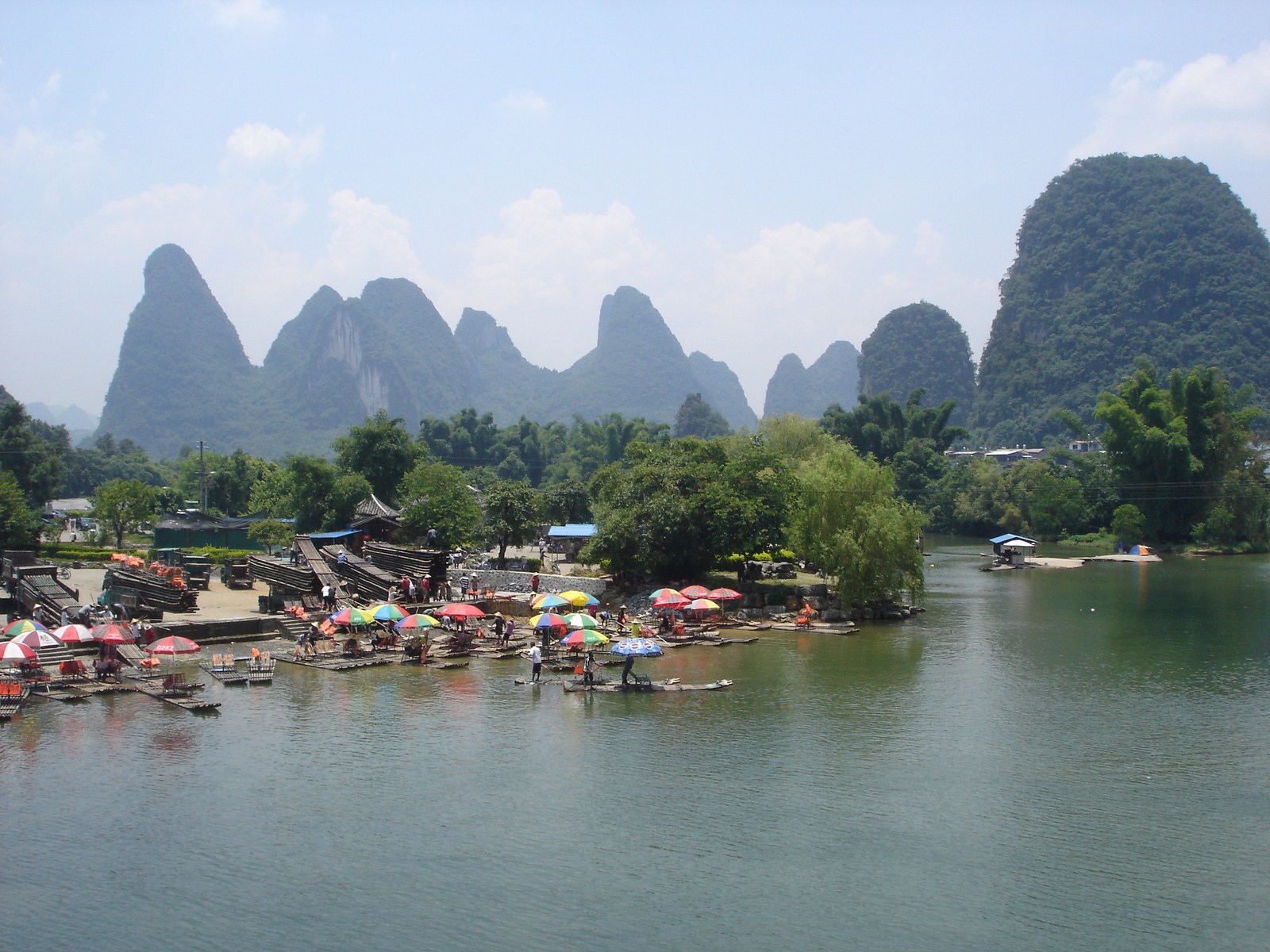
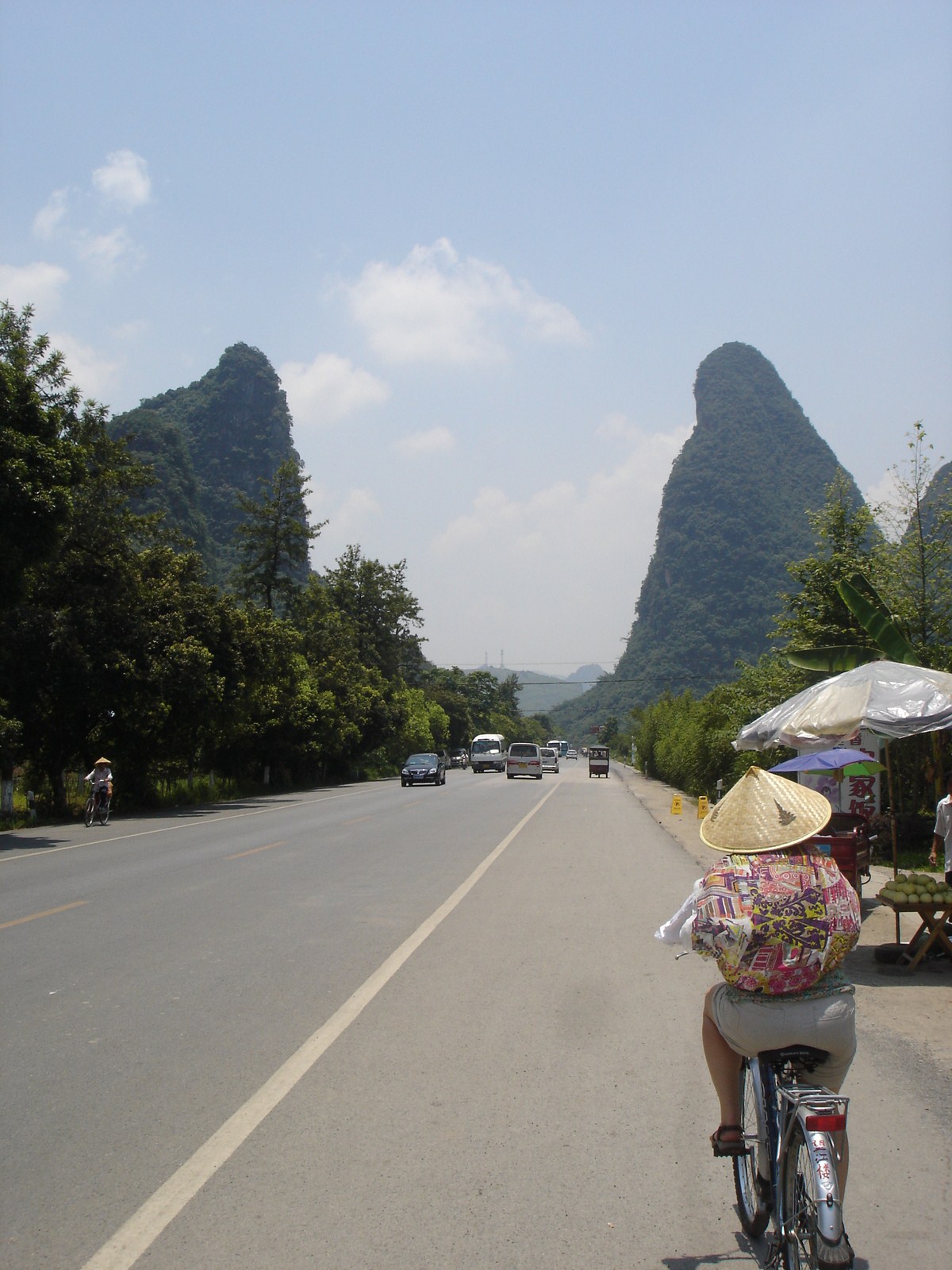
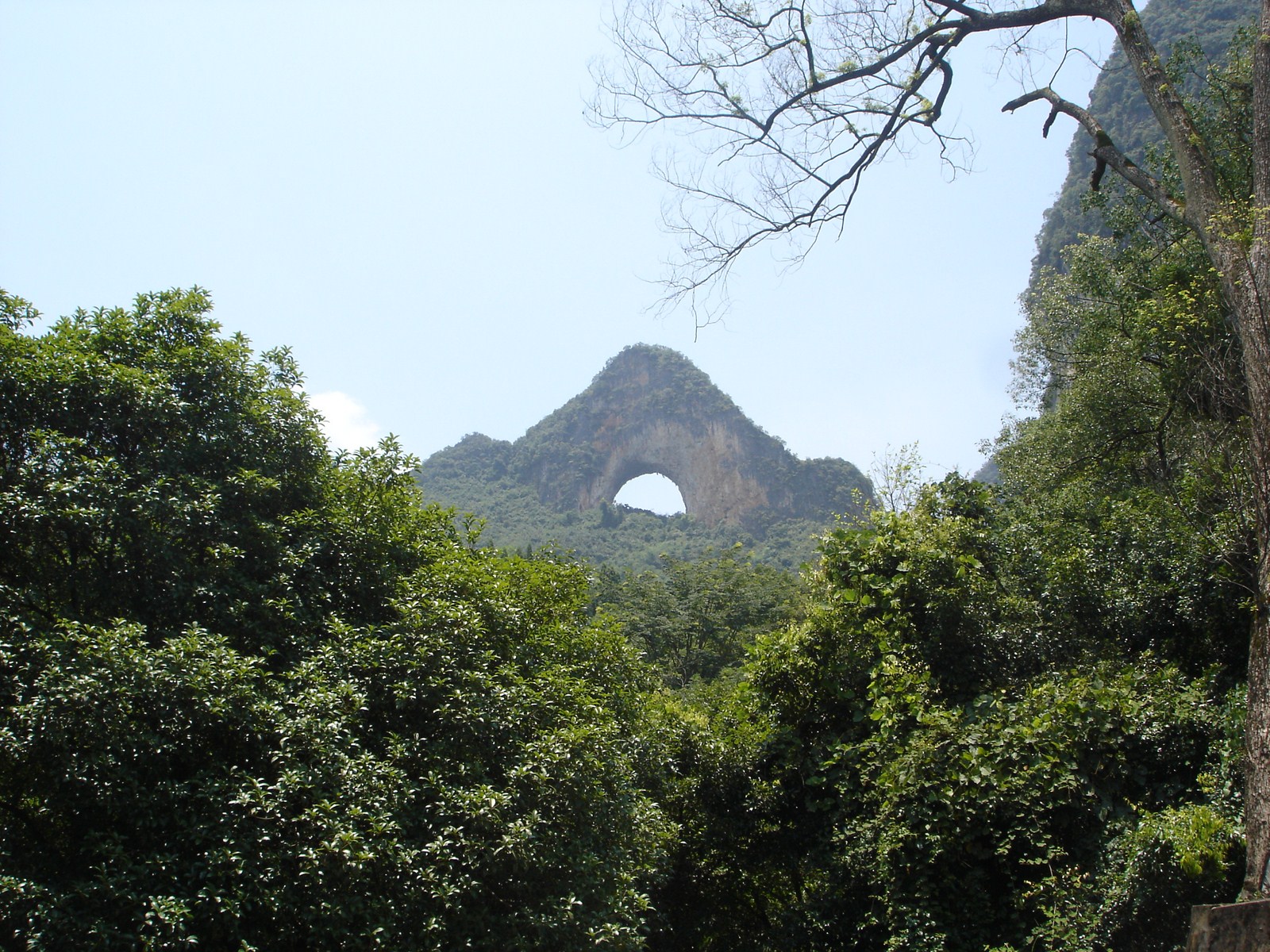
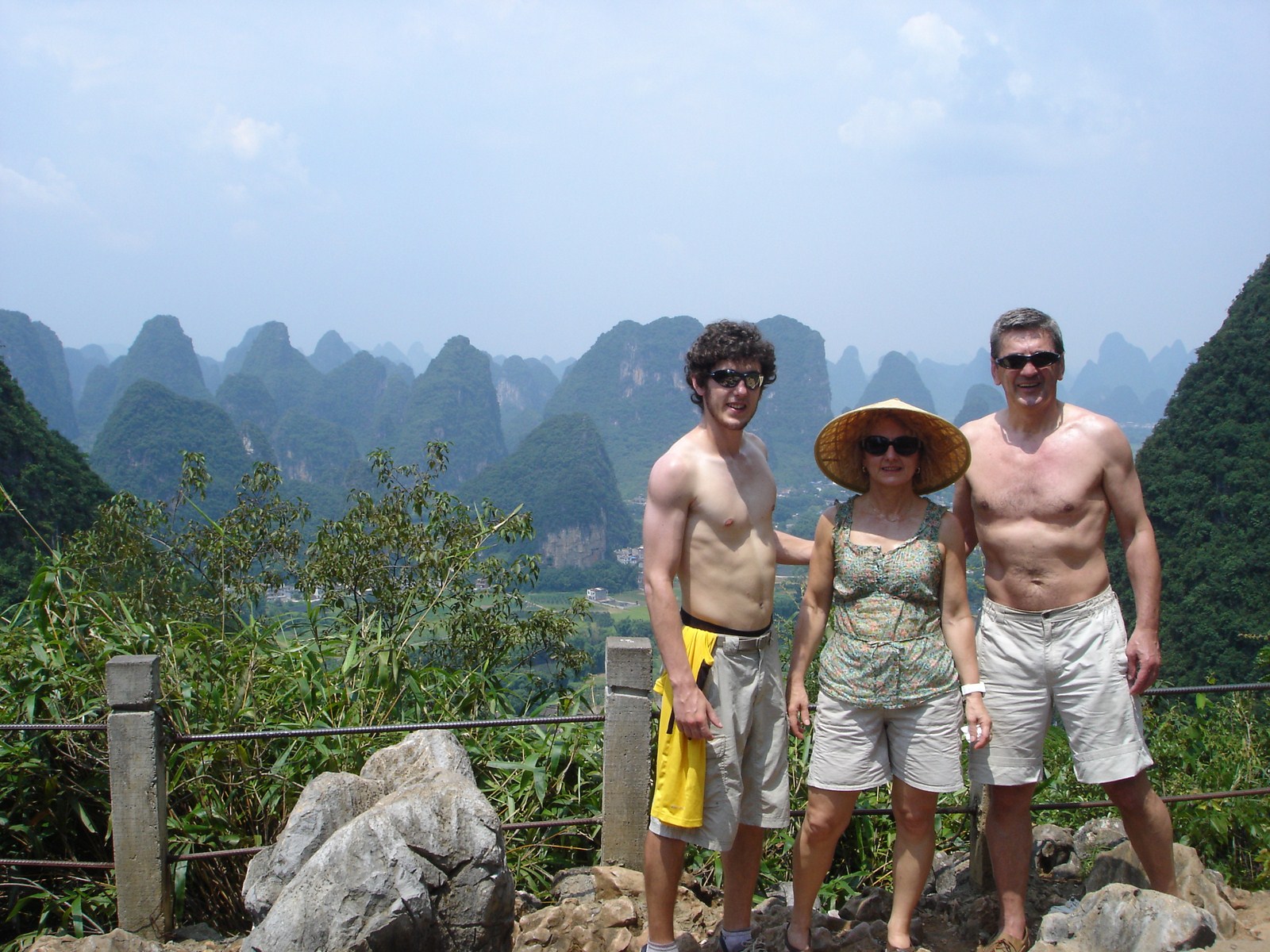
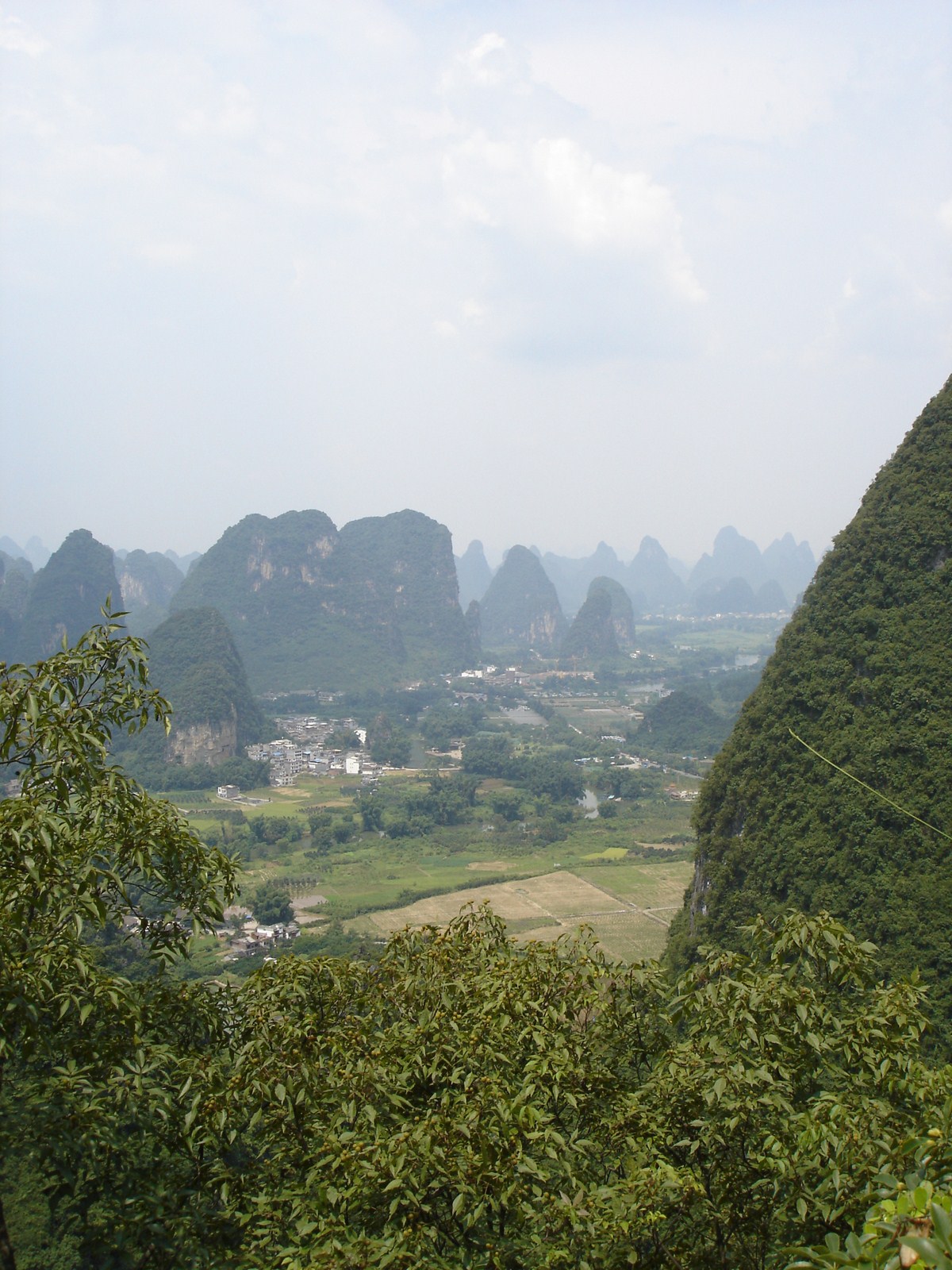
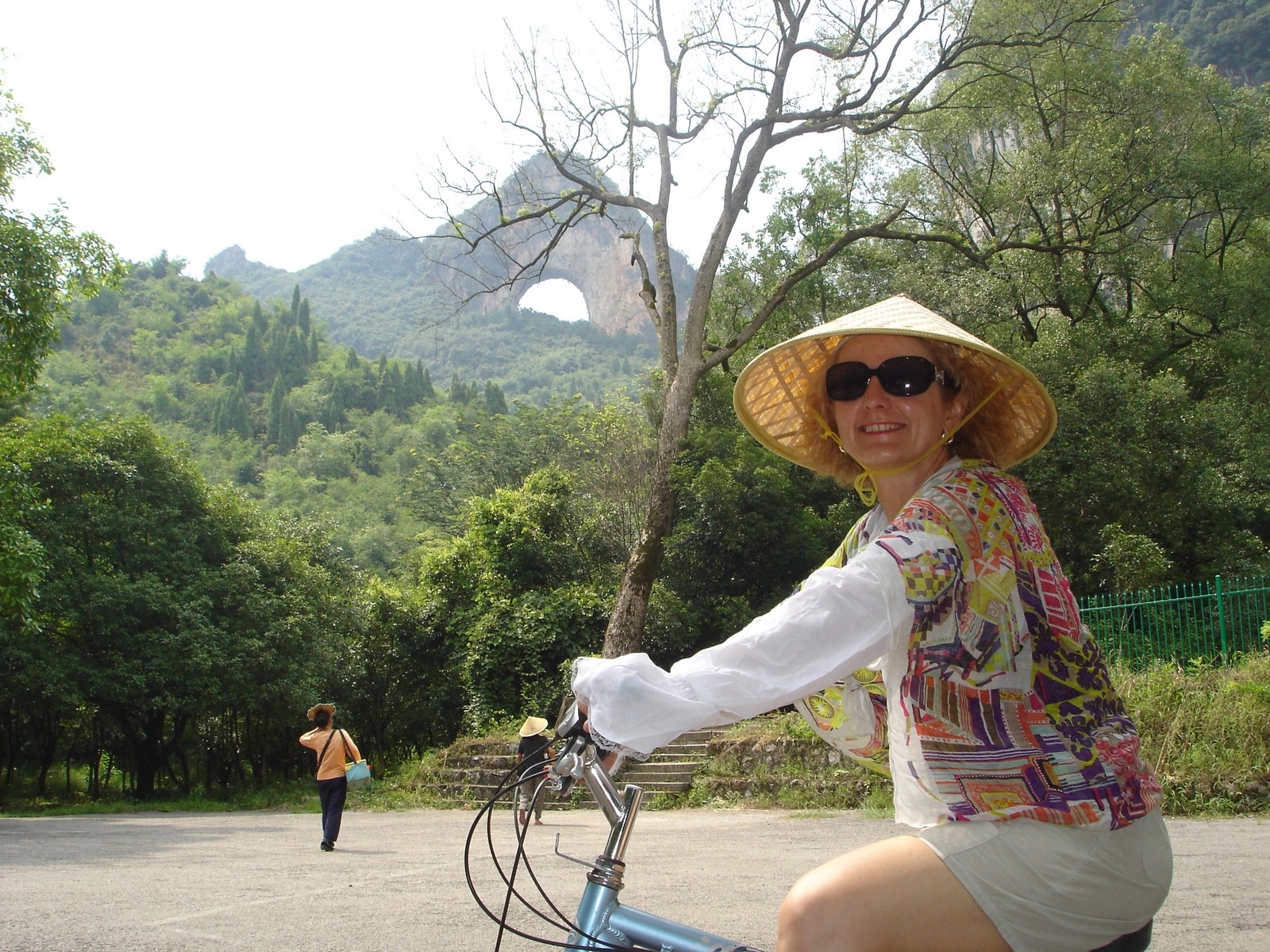
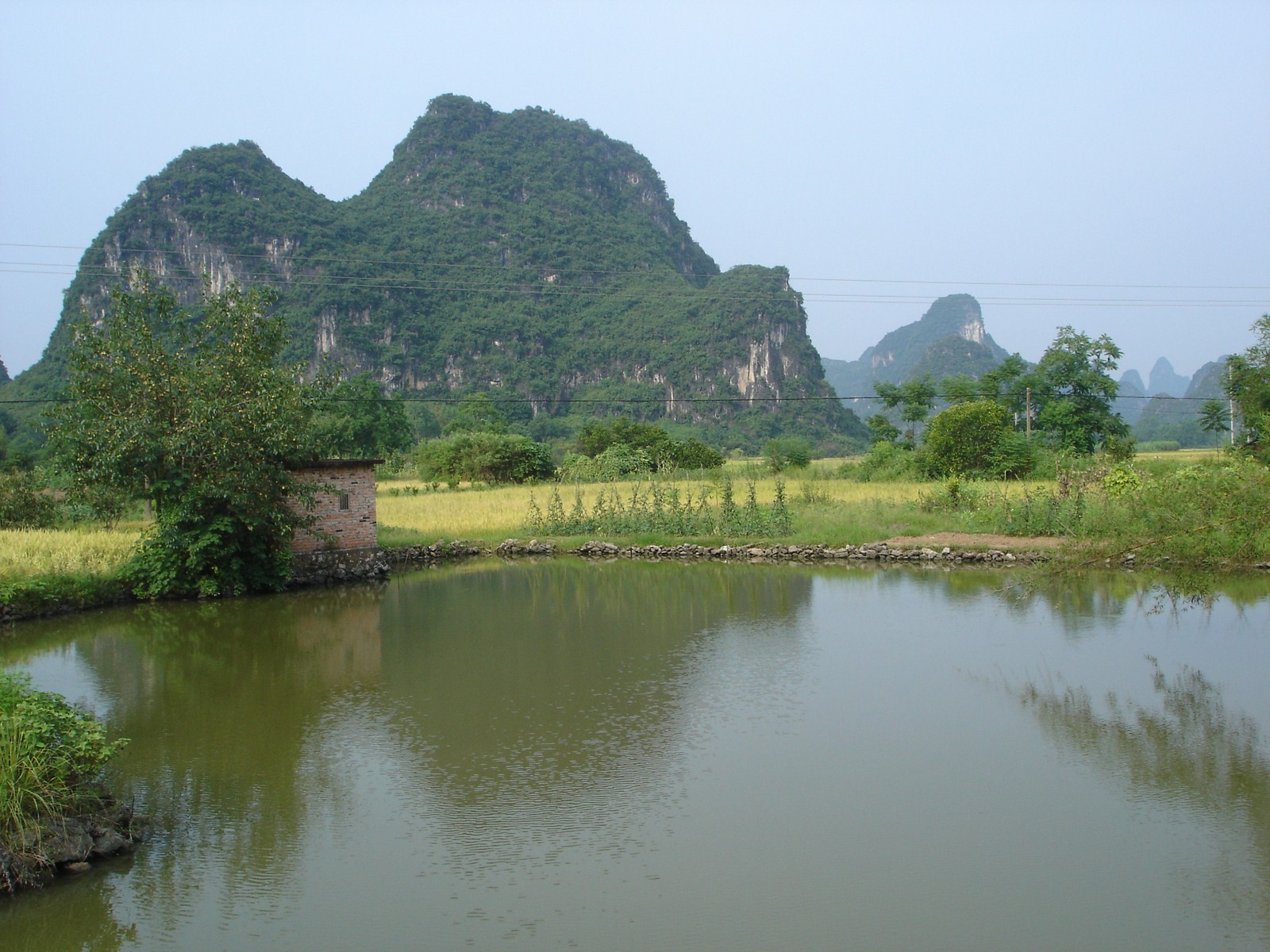
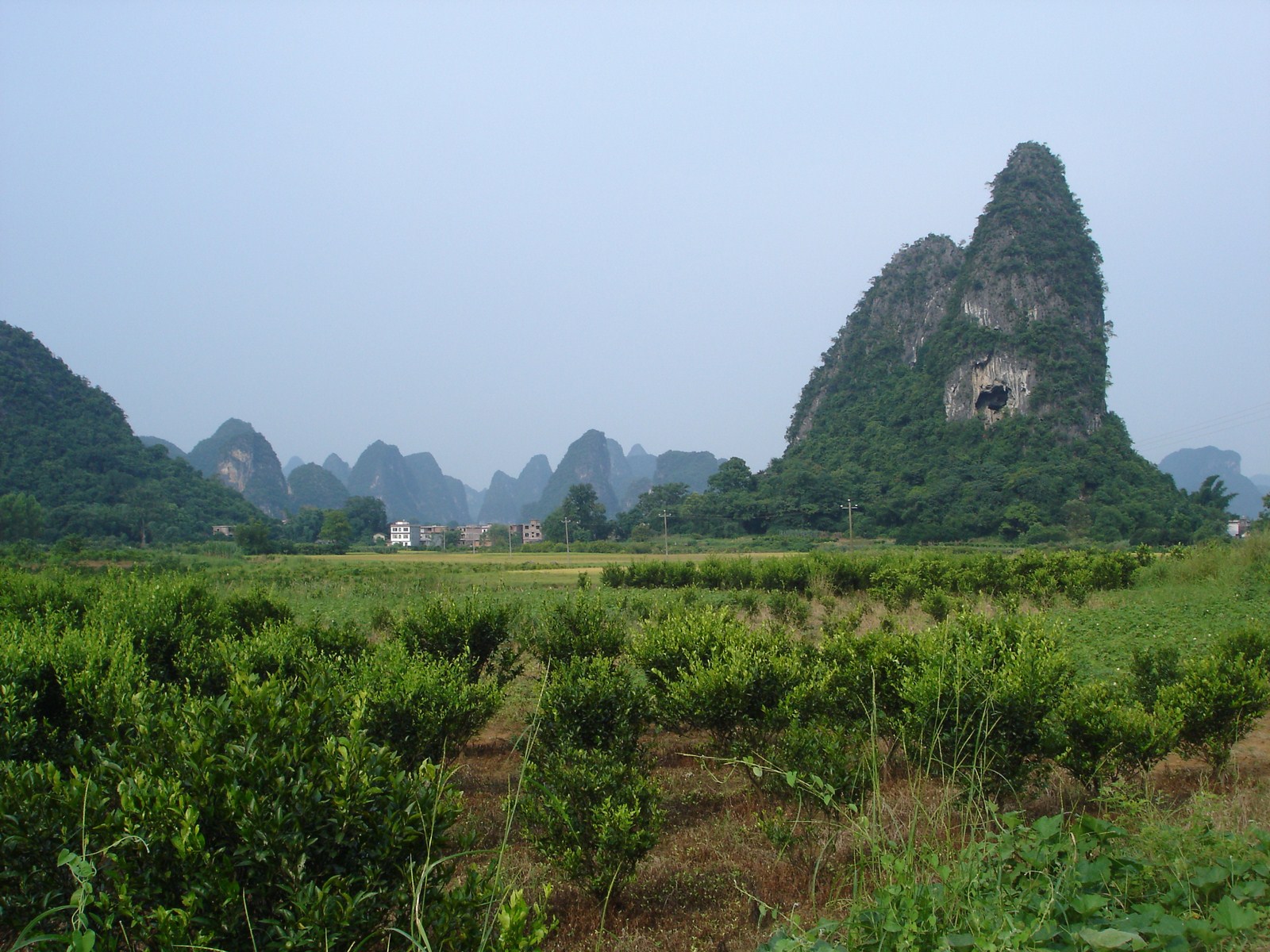
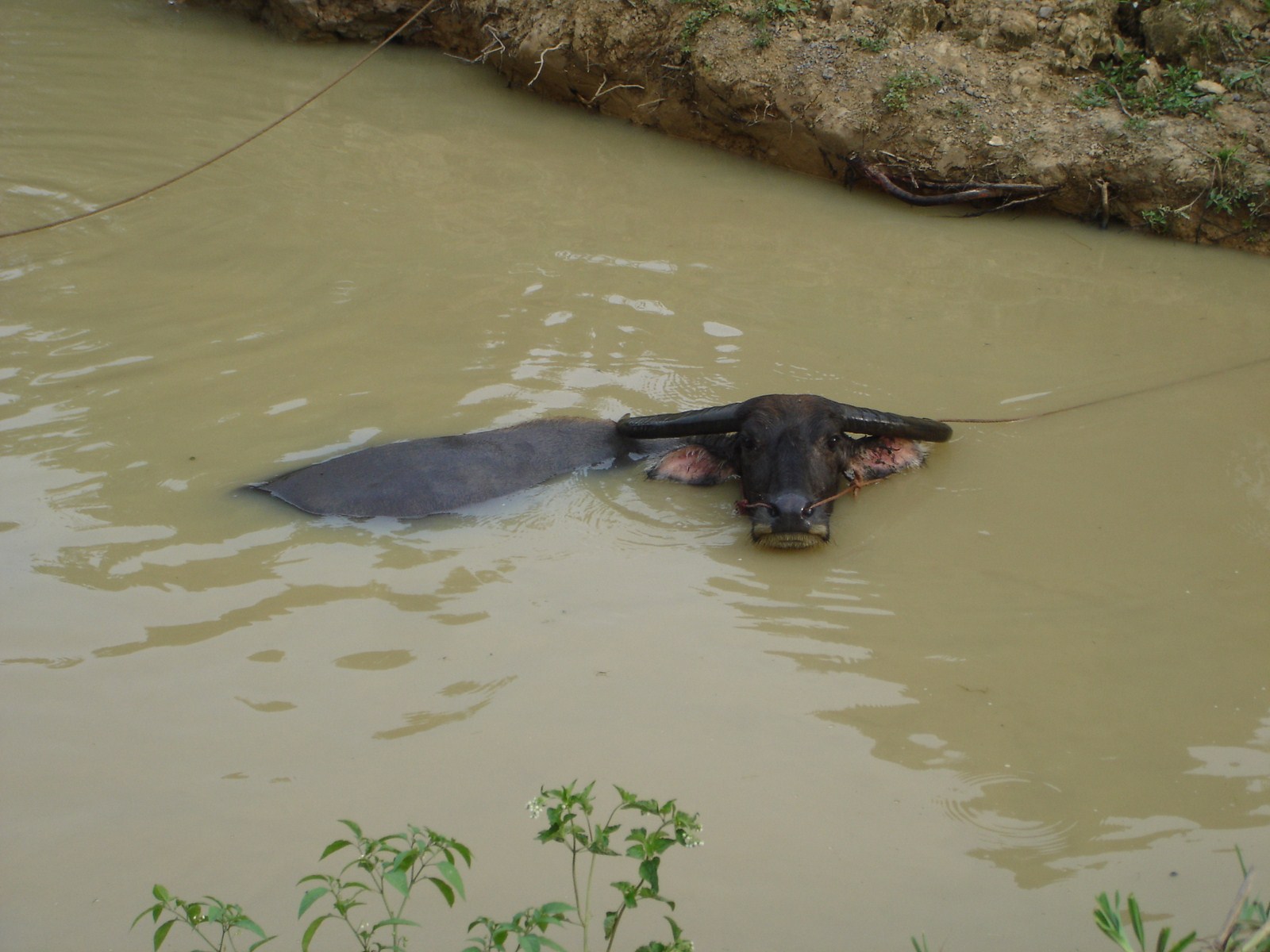
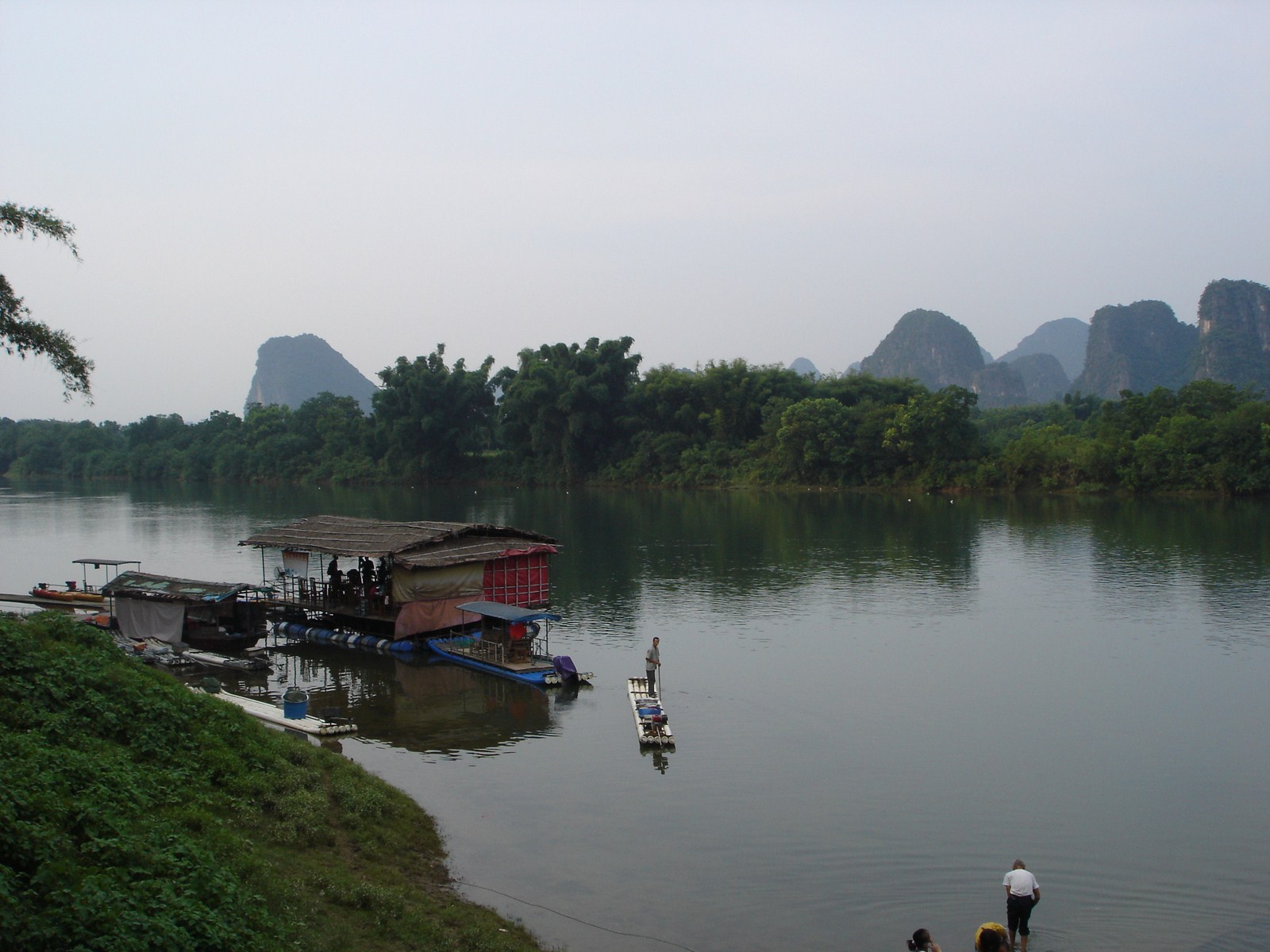
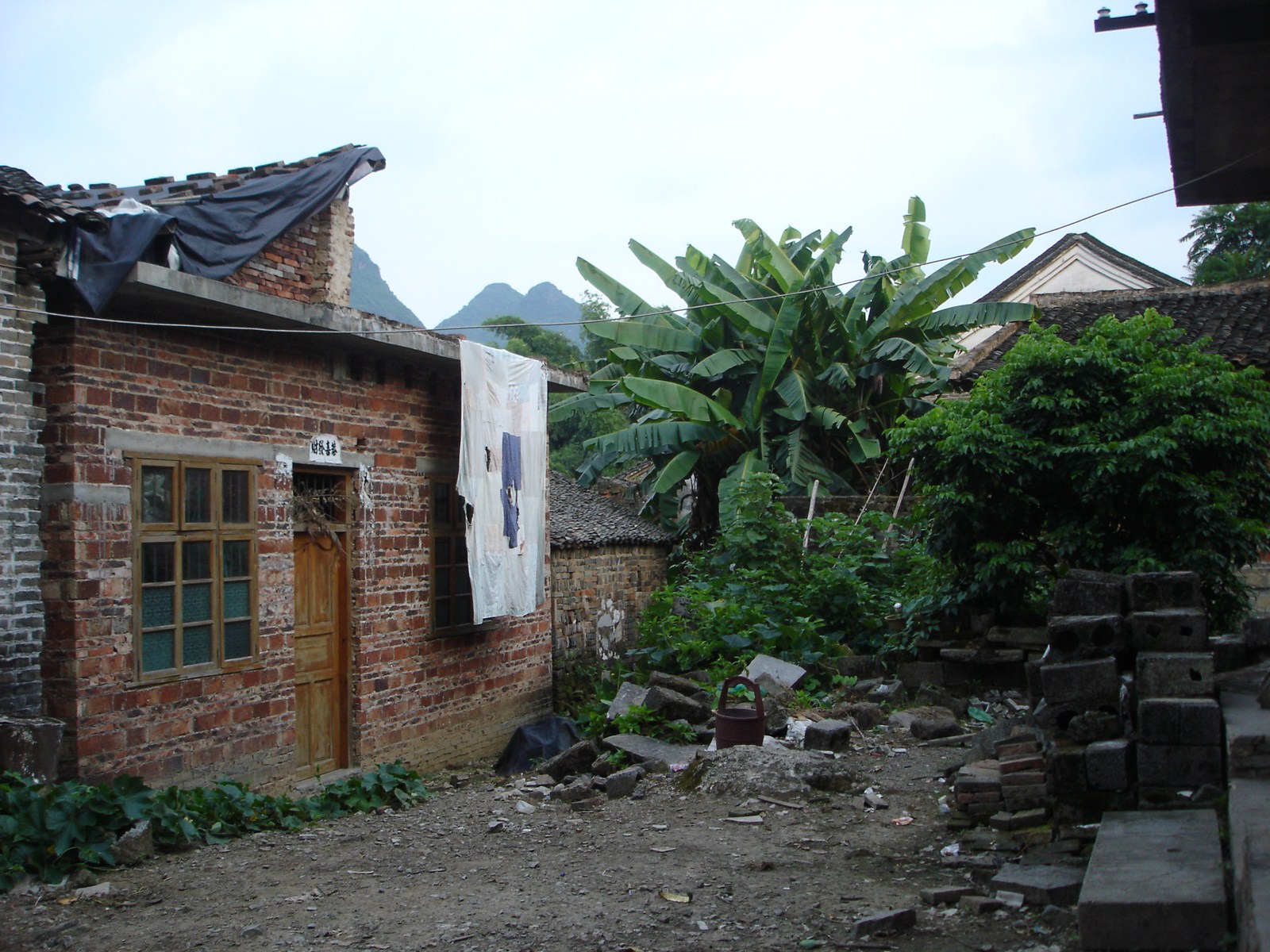
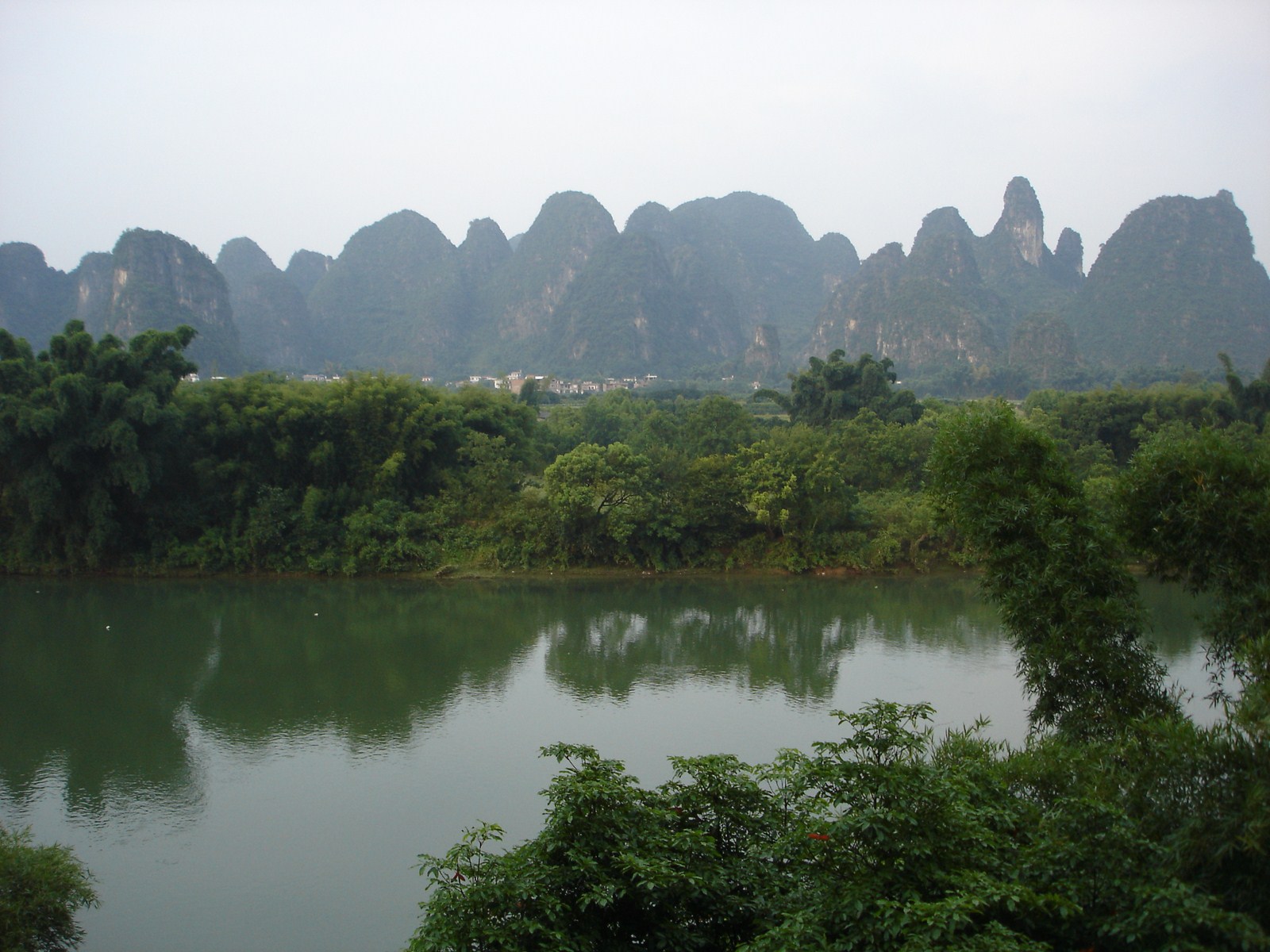
Voici la première des trois galeries (une par jour) dédiée à Yangshuo, un des plus beaux paysages de Chine et du monde. Après une petite vue de l'intérieur, balade au sud de la ville avec traversée de la rivière Yulong et escapade au MoonHill (la montagne percée d'un trou). |
|
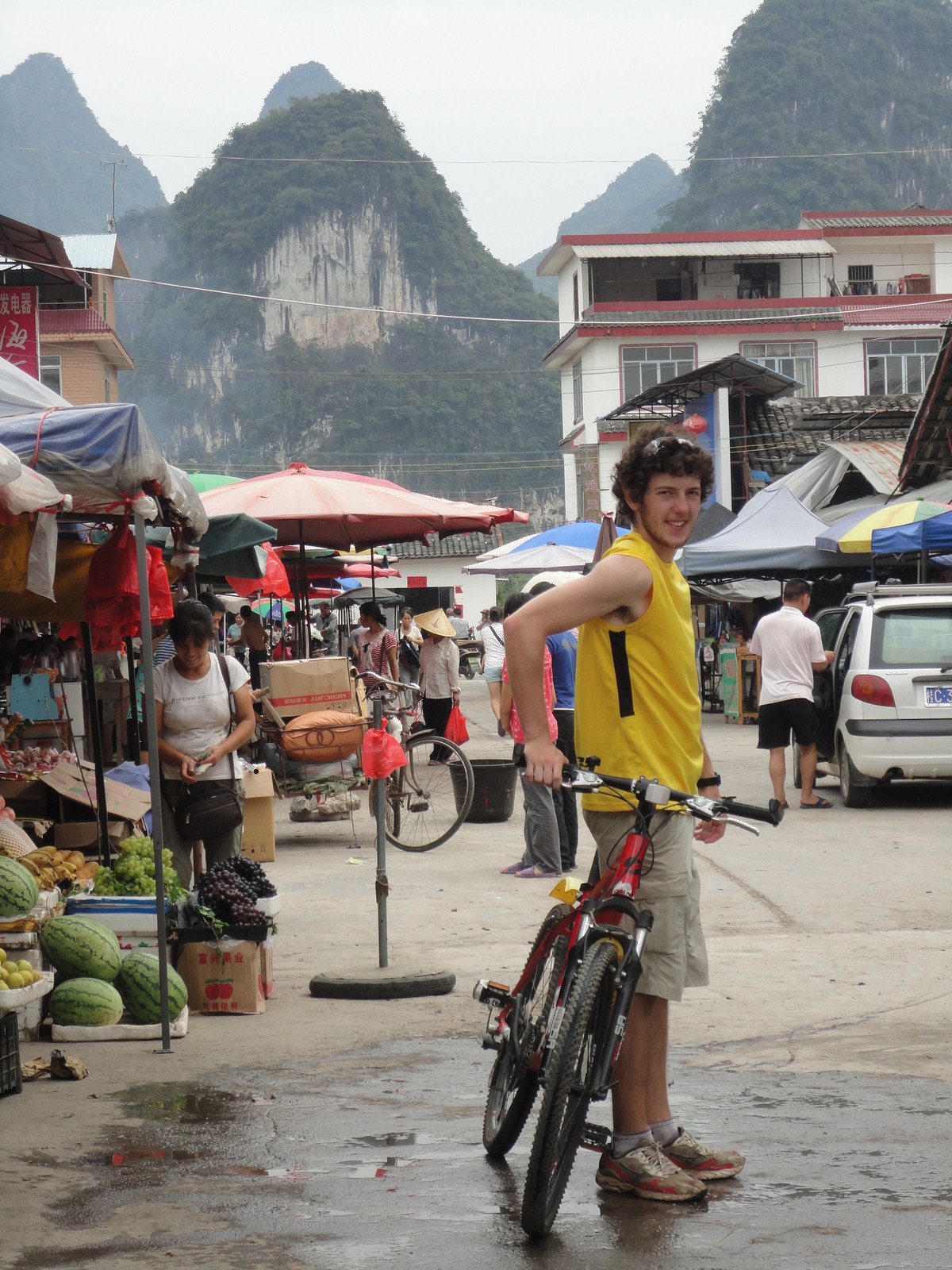
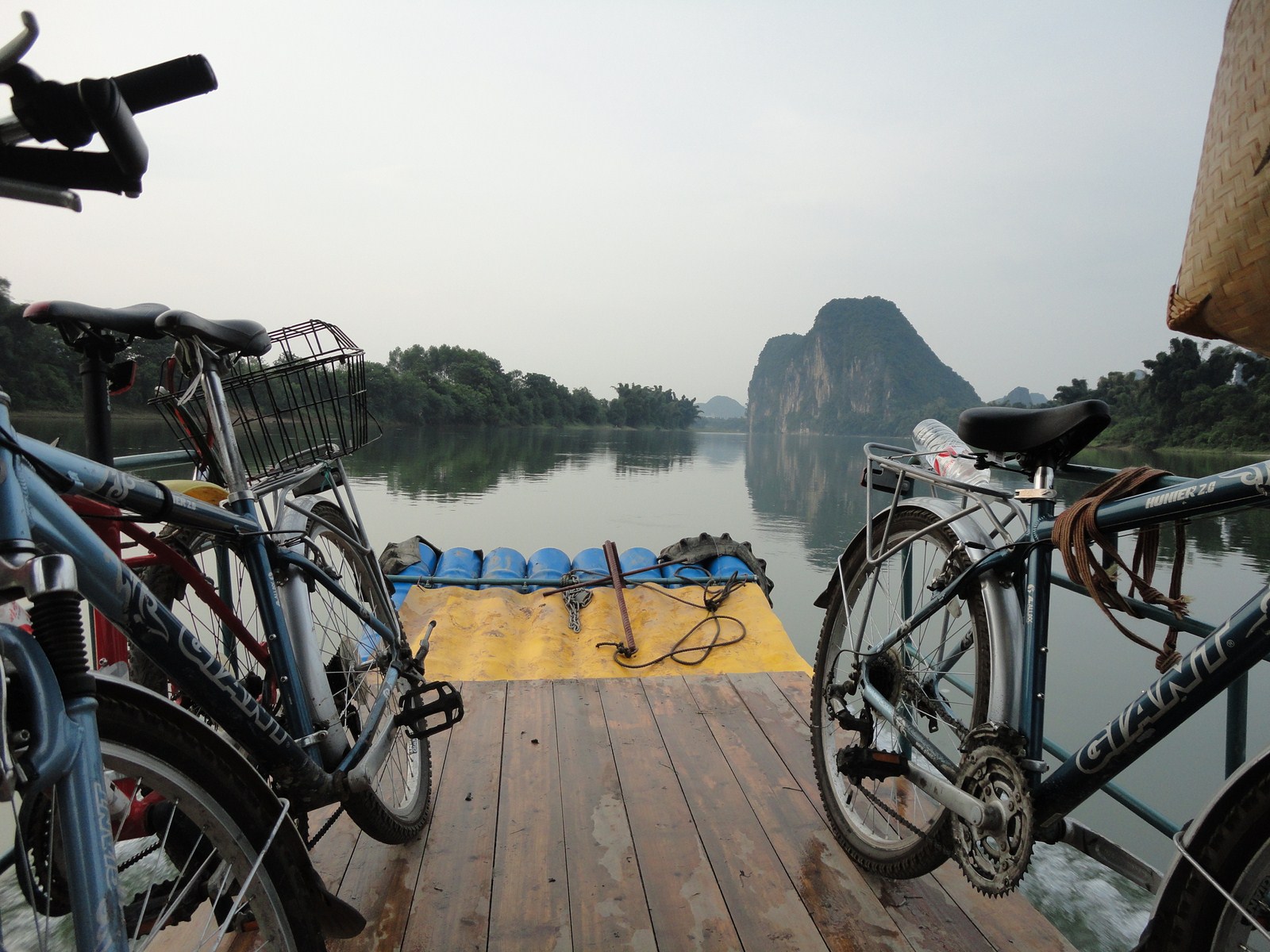
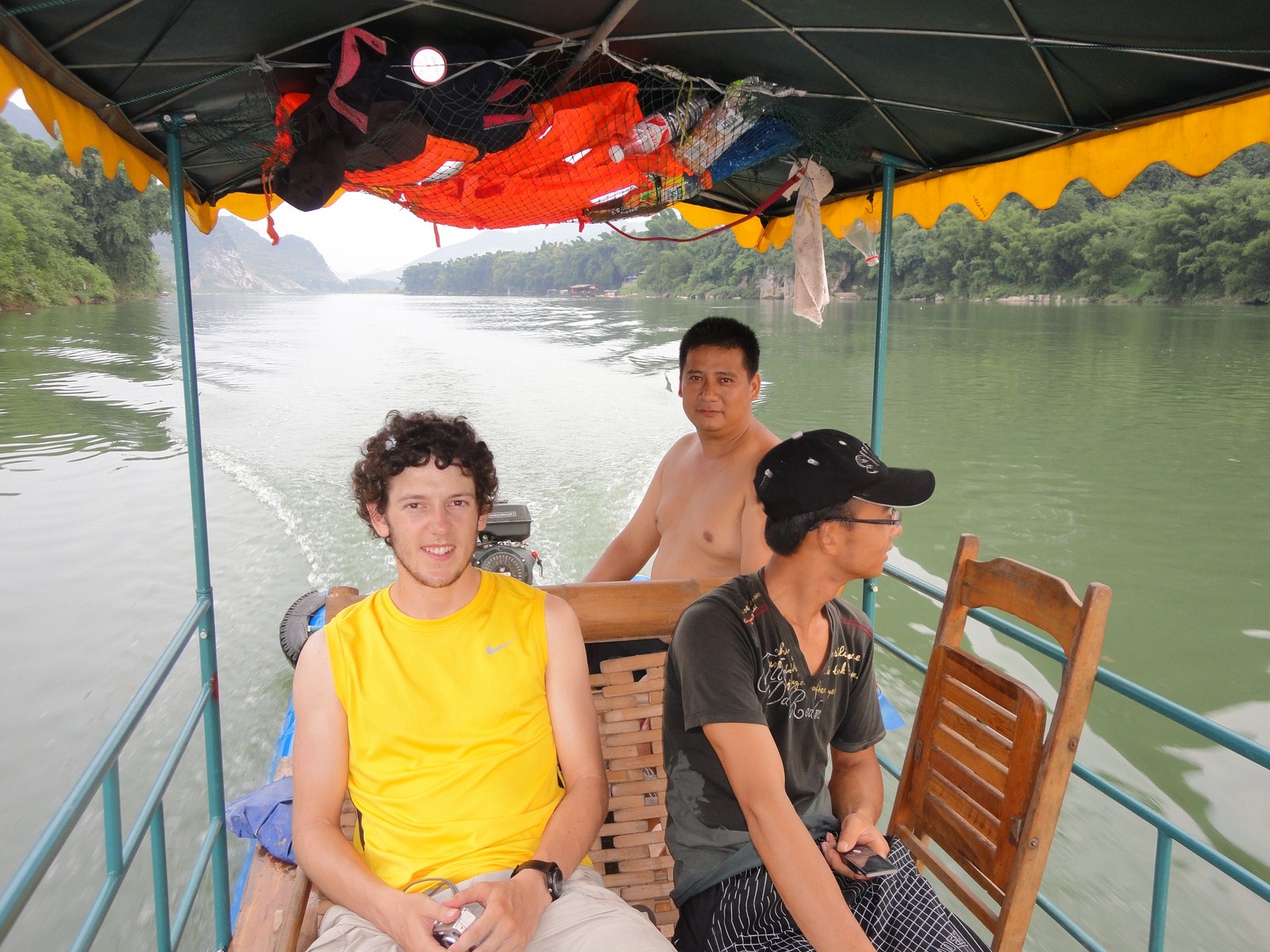
Petit arrêt pour la visite du marché de Gaotian, suivit d'une traversée en direction de l'est pour atterrir dans le petit village de Liugong, et finalement d'un retour vers la ville sur un radeau-bambou. |














































Comments
U.S. charges sibling leaders of ruthless
Crime
U.S. charges sibling leaders of ruthless Mexico cartel, offers $8 million reward for information leading to their capture
Updated on: April 16, 2025 / 7:02 AM EDT / CBS/AP
kraken tor
Federal authorities said Tuesday that they have indicted the top two leaders of a Mexican drug cartel and are offering up to $8 million rewards for information leading to their capture and conviction.
kraken через tor
Johnny Hurtado Olascoaga and Jose Alfredo Hurtado Olascoaga, are accused of participating in a conspiracy to manufacture cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine and fentanyl and importing and distributing the drugs in the United States, authorities said during a news conference in Atlanta. The newly unsealed three-count indictment was returned by a grand jury in September.
kraken через tor
The two brothers are the leaders of La Nueva Familia Michoacana, a Mexican cartel that was formally designated by the U.S. government in February as a "foreign terrorist organization," authorities said.
"If you contribute to the death of Americans by peddling poison into our communities, we will work relentlessly to find you and bring you to justice," Attorney General Pam Bondi said in a statement.
The State Department is offering up to $5 million for information leading to the arrest and/or conviction of Johnny Hurtado Olascoaga and up to $3 million for information about Jose Alfredo Hurtado Olascoaga, who also goes by the name "The Strawberry." Both men are believed to be in Mexico, officials said.
Separately the U.S. Treasury announced new sanctions Wednesday against the two men and well as two other alleged leaders of the cartel, which the U.S. designates as a "foreign terrorist organization."
In addition to drug trafficking, the Familia Michoacana cartel has also engaged in extortions, kidnappings and murders, according to U.S. prosecutors.
kraken4qzqnoi7ogpzpzwrxk7mw53n5i56loydwiyonu4owxsh4g67yd.onion
https://kraken3yvbvzmhytnrnuhsy772i6dfobofu652e27f5hx6y5cpj7rgd.com
казино онлайн беларусь
Лучшие казино онлайн в Беларуси, получайте удовольствие от игры, с нетерпением ожидают.
Лучшие онлайн-игры из Беларуси, в любое время и в любом месте, для настоящих азартных игроков.
Реальные выигрыши в онлайн-казино, лицензированные заведения, достигайте успеха.
Самые надежные онлайн-казино в Беларуси, каждый день.
Играйте в любимые игры в казино онлайн, от карточных до настольных игр, для истинных ценителей.
Новые онлайн-казино Беларуси, для любителей хорошей игры.
Соберите все бонусы и акции, только для вас.
Топ онлайн-игр в белорусских казино, всегда готовы к игре, откройте для себя мир азартных игр.
Как выбрать лучшее казино, по играм на деньги.
Ваш шанс на удачу здесь, не упустите возможность выиграть.
казино беларусь [url=https://kazino-on-line.by/]казино беларусь[/url] .
XRumer seo run
https://politedriver.com/
Pre-eminent SEO services near me
https://politedriver.com/sankt-peterburg
Placing the site on quality trust sites
https://politedriver.com/
Placing the site on quality trust sites
https://politedriver.com/sankt-peterburg
Mailing
https://politedriver.com/sankt-peterburg
Search Engine Optimization
https://politedriver.com/
XRumer seo run
https://politedriver.com/
Search Engine Optimization
https://politedriver.com/sankt-peterburg
kraken7jmgt7yhhe2c4iyilthnhcugfylcztsdhh7otrr6jgdw667pqd
Kate Winslet had a surprising ‘Titanic’ reunion while producing her latest film ‘Lee’
kraken2trfqodidvlh4aa337cpzfrhdlfldhve5nf7njhumwr7instad
Kate Winslet is sharing an anecdote about a “wonderful” encounter she recently had with someone from her star-making blockbuster film “Titanic.”
The Oscar winner was a guest on “The Graham Norton Show” this week, where she discussed her new film “Lee,” in which she plays the fashion model-turned-war photographer Lee Miller from the World War II era.
https://kraken6gf6o4rxewycqwjgfchzgxyfeoj5xafqbfm4vgvyaig2vmxvyd-onion.net
kraken7jmgt7yhhe2c4iyilthnhcugfylcztsdhh7otrr6jgdw667pqd.onion
Winslet recounted that while she had previously executive produced a number of her projects, “Lee” was the first movie where she served as a full-on producer. That required her involvement from “beginning to end,” including when the film was scored in post-production.
She explained to Norton that when she attended the recording of the film’s score in London, while looking at the 120-piece orchestra, she saw someone who looked mighty familiar to her.
“I’m looking at this violinist and I thought, ‘I know that face!’” she said.
At one point, other musicians in the orchestra pointed to him while mouthing, “It’s him!” to her, and it continued to nag at Winslet, prompting her to wonder, “Am I related to this person? Who is this person?”
Finally, at the end of the day, the “Reader” star went in to where the orchestra was to meet the mystery violinist, and she was delighted to realize he was one of the violinists who played on the ill-fated Titanic ocean liner as it sank in James Cameron’s classic 1997 film.
“It was that guy!” Winslet exclaimed this week, later adding, “it was just wonderful” to see him again.
“We had so many moments like that in the film, where people I’ve either worked with before, or really known for a long time, kind of grown up in the industry with, they just showed up for me, and it was incredible.”
“Lee” released in theaters in late September, and is available to rent or buy on AppleTV+ or Amazon Prime.
Georgia journalist jailed over protests against pro-Russian gove
Tbilisi, Georgia — Jailed journalist Mzia Amaghlobeli gets weaker every day as her hunger strike has reached three weeks in Rustavi, a town near the Georgian capital of Tbilisi, her lawyer says. Now the 49-year-old is having difficulty walking the short distance from her cell to the room where they usually meet, and human rights officials, colleagues and family fear for her life.
kra26.at
Amaghlobeli was arrested Jan. 12 during an anti-government protest in the coastal city of Batumi, one of over 40 people in custody on criminal charges from a series of demonstrations that have hit the South Caucasus nation of 3.7 million in recent months.
kra25.cc
The political turmoil follows a parliamentary election that was won by the ruling Georgian Dream party, although its opponents allege the vote was rigged.
Protests highlight battle over Georgia's future. Here's why it matters.
Its outcome pushed Georgia further into Russia's orbit of influence. Georgia aspired to join the European Union, but the party suspended accession talks with the bloc after the election.
As it sought to cement its grip on power, Georgian Dream has cracked down on freedom of assembly and expression in what the opposition says is similar to President Vladimir Putin's actions in neighboring Russia, its former imperial ruler.
kra26 cc
https://kpa25.at
Georgia journalist jailed over protests against pro-Russian gove
Tbilisi, Georgia — Jailed journalist Mzia Amaghlobeli gets weaker every day as her hunger strike has reached three weeks in Rustavi, a town near the Georgian capital of Tbilisi, her lawyer says. Now the 49-year-old is having difficulty walking the short distance from her cell to the room where they usually meet, and human rights officials, colleagues and family fear for her life.
kra30 at
Amaghlobeli was arrested Jan. 12 during an anti-government protest in the coastal city of Batumi, one of over 40 people in custody on criminal charges from a series of demonstrations that have hit the South Caucasus nation of 3.7 million in recent months.
kra25 cc
The political turmoil follows a parliamentary election that was won by the ruling Georgian Dream party, although its opponents allege the vote was rigged.
Protests highlight battle over Georgia's future. Here's why it matters.
Its outcome pushed Georgia further into Russia's orbit of influence. Georgia aspired to join the European Union, but the party suspended accession talks with the bloc after the election.
As it sought to cement its grip on power, Georgian Dream has cracked down on freedom of assembly and expression in what the opposition says is similar to President Vladimir Putin's actions in neighboring Russia, its former imperial ruler.
kra27 at
https://kra27-at.ru
Search Engine Optimization
https://krk-finance.ru/
Search Engine Optimization
https://zaimodobren.ru/
Best SEO services near me
https://simpleswapp.org/
Placing the site on quality trust sites
https://zaimodobren.ru/
XRumer seo skip out
https://krk-finance.ru/
Placing the site on quality trust sites
https://simpleswapp.org/
Search Engine Optimization
https://simpleswapp.org/
Seo service
https://simpleswapp.org/
Seo help
https://fixedfloatt.com
Striking images showing environmental destruction aim to ‘inspir
Tree-covered mountains rise behind a pile of trash, children run through the orange haze of a dust storm, and a billboard standing on parched earth indicates where the seashore used to be before desertification took hold. These striking images, exhibited as part of the Right Here, Right Now Global Climate Summit, show the devastating effects of climate change.
кракен вход
The summit, held at the University of Oxford in the UK and supported by UN Human Rights (OHCHR), aims to reframe climate change as a human rights crisis and spotlight climate solutions. It works with everyone from policymakers to artists to get the message across.
“Photographers document the human rights impacts of climate change, helping to inform the public and hold governments and businesses accountable,” said Volker Turk, UN High Commissioner for the OHCHR, via email. “The Right Here, Right Now Global Climate Summit shows the power of collective action — uniting storytellers, scientists, indigenous leaders, and others to advance climate solutions rooted in human rights.”
Coinciding with World Environment Day on June 5, the exhibition — titled “Photography 4 Humanity: A Lens on Climate Justice” — features the work of 31 photographers from across the globe, all documenting the effects of global warming and environmental pollution on their own communities.
Climate change disproportionately affects vulnerable populations around the world. Despite emitting far fewer greenhouse gases, low-income nations are suffering the most from extreme weather events and have fewer resources to adapt or recover.
Photographs at the exhibition show the effects of desertification, flooding and plastic pollution. A black and white image shows the ruins of a house in West Bengal, India, sloping towards the Ganges River, with the owner sitting alongside. Riverbank erosion is degrading the environment and displacing communities in the area. Photographer Masood Sarwer said in a press release that the photo depicts the “slow violence” of climate change: “These are not sudden disasters, but slow-moving, relentless ones — shaping a new category of environmental refugees.”
Another photo, taken by Aung Chan Thar, shows children fishing for trash in Inle Lake, Myanmar. The lake was once a pristine natural wonder but now faces the growing threat of plastic pollution. “This image of children cleaning the water symbolizes the importance of education and collective action in preserving our environment for a sustainable future,” he said.
Organizers hope that the exhibition will help to humanize the climate crisis. “Our mission is to inspire new perspectives through photography,” said Pauline Benthede, global vice president of artistic direction and exhibitions at Fotografiska, the museum of photography, art and culture that is curating the exhibition at the summit. “It draws attention to the human rights issue at the heart of global warming, which affects both the world’s landscapes and the people that live within them.”
“Photography is the most influential and inclusive art form of our times and has the power to foster understanding and inspire action,” she added.
Seo service
https://pancakeswapdefi.org
XRumer seo run
https://fixedfloatt.com
XRumer seo run
https://fixedfloatt.com
Seo service
https://fixedfloatt.com
Search Engine Optimization
https://pancakeswapdefi.org
Excellent SEO services close me
https://simple-swap.top
Placing the site on quality trust sites
https://jup-dex.org
Best SEO services near me
https://simple-swap.top
Placing the site on quality trust sites
https://jup-dex.org
NASA scientists describe ‘absolute sh*tshow’ at agency as Trump
NASA scientists are in a state of anxious limbo after the Trump administration proposed a budget that would eliminate one of the United States’ top climate labs – the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, or GISS – as a standalone entity.
kra34 cc
In its place, it would move some of the lab’s functions into a broader environmental modeling effort across the agency.
Career specialists are now working remotely, awaiting details and even more unsure about their future at the lab after they were kicked out of their longtime home in New York City last week. Closing the lab for good could jeopardize its value and the country’s leadership role in global climate science, sources say.
“It’s an absolute sh*tshow,” one GISS scientist said under condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak to the media. “Morale at GISS has never been lower, and it feels for all of us that we are being abandoned by NASA leadership.”
“We are supposedly going to be integrated into this new virtual NASA modeling institute, but (we have) no idea what that will actually look like,” they said.
NASA is defending its budget proposal, with a nod toward the lab’s future.
“NASA’s GISS has a significant place in the history of space science and its work is critical for the Earth Science Division, particularly as the division looks to the future of its modeling work and capabilities,” NASA spokesperson Cheryl Warner said in a statement.
“Fundamental contributions in research and applications from GISS directly impact daily life by showing the Earth system connections that impact the air we breathe, our health, the food we grow, and the cities we live in,” Warner said.
GISS has a storied history in climate science on the global scale.
James Hansen, a former director, first called national attention to human-caused global warming at a Senate hearing during the hot summer of 1988. The lab, founded in 1961, is still known worldwide for its computer modeling of the planet that enable scientists to make projections for how climate change may affect global temperatures, precipitation, extreme weather events and other variables.
Натяжные потолки ПВХ
Советую рекомендовать сайт...
Как выбрать натяжной потолок для зала?
Оцените наш труд!
Search Engine Optimization
https://jup-dex.org
Seo help
https://simple-swap.top
пинап
Scientists mapped what happens if a crucial system of ocean currents collapses. The weather impact would be extreme
pin up
The collapse of a crucial network of Atlantic Ocean currents could push parts of the world into a deep freeze, with winter temperatures plunging to around minus 55 degrees Fahrenheit in some cities, bringing “profound climate and societal impacts,” according to a new study.
There is increasing concern about the future of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation — known as the AMOC — a system of currents that works like a giant conveyor belt, pulling warm water from the Southern Hemisphere and tropics to the Northern Hemisphere, where it cools, sinks and flows back south.
Multiple studies suggest the AMOC is weakening with some projecting it could even collapse this century as global warming disrupts the balance of heat and salinity that keeps it moving. This would usher in huge global weather and climate shifts — including plunging temperatures in Europe, which relies on the AMOC for its mild climate.
What’s less clear, however, is how these impacts will unfold in a world heated up by humans burning fossil fuels.
“What if the AMOC collapses and we have climate change? Does the cooling win or does the warming win?” asked Rene van Westen, a marine and atmospheric researcher at Utrecht University in the Netherlands and co-author of the paper published Wednesday in the Geophysical Research Letters journal.
This new study is the first to use a modern, complex climate model to answer the question, he told CNN.
The researchers looked at a scenario where the AMOC weakens by 80% and the Earth is around 2 degrees Celsius warmer than the period before humans began burning large amounts of fossil fuels. The planet is currently at 1.2 degrees of warming.
They focused on what would happen as the climate stabilized post-collapse, multiple decades into the future.
Even in this hotter world, they found “substantial cooling” over Europe with sharp drops in average winter temperatures and more intense cold extremes — a very different picture than the United States, where the study found temperatures would continue to increase even with an AMOC collapse.
Sea ice would spread southward as far as Scandinavia, parts of the United Kingdom and the Netherlands, the research found. This would have a huge impact on cold extremes as the white surface of the ice reflects the sun’s energy back into space, amplifying cooling.
The scientists have created an interactive map to visualize the impacts of an AMOC collapse across the globe.
Placing the site on quality trust sites
https://jup-dex.org
Seo service
https://simple-swap.top
NASA scientists describe ‘absolute sh*tshow’ at agency as Trump
NASA scientists are in a state of anxious limbo after the Trump administration proposed a budget that would eliminate one of the United States’ top climate labs – the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, or GISS – as a standalone entity.
kra34.cc
In its place, it would move some of the lab’s functions into a broader environmental modeling effort across the agency.
Career specialists are now working remotely, awaiting details and even more unsure about their future at the lab after they were kicked out of their longtime home in New York City last week. Closing the lab for good could jeopardize its value and the country’s leadership role in global climate science, sources say.
“It’s an absolute sh*tshow,” one GISS scientist said under condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak to the media. “Morale at GISS has never been lower, and it feels for all of us that we are being abandoned by NASA leadership.”
“We are supposedly going to be integrated into this new virtual NASA modeling institute, but (we have) no idea what that will actually look like,” they said.
NASA is defending its budget proposal, with a nod toward the lab’s future.
“NASA’s GISS has a significant place in the history of space science and its work is critical for the Earth Science Division, particularly as the division looks to the future of its modeling work and capabilities,” NASA spokesperson Cheryl Warner said in a statement.
“Fundamental contributions in research and applications from GISS directly impact daily life by showing the Earth system connections that impact the air we breathe, our health, the food we grow, and the cities we live in,” Warner said.
GISS has a storied history in climate science on the global scale.
James Hansen, a former director, first called national attention to human-caused global warming at a Senate hearing during the hot summer of 1988. The lab, founded in 1961, is still known worldwide for its computer modeling of the planet that enable scientists to make projections for how climate change may affect global temperatures, precipitation, extreme weather events and other variables.
ПВХ натяжные потолки
Советую хороший материал сайта...
Где заказать установку натяжного потолка в Москве?
Также оставлаяйте свое мнение!
Потолки натяжные
Рекомендую отличный материал сайта...
Какой натяжной потолок лучше выбрать для кухни матовый или глянцевый отзывы?
Вы можете оставить свою оценку!
ПВХ потоки
Советую блог сайта...
Натяжной потолок глянцевый или матовый Какой лучше?
Оставляйте коментарии!
Search Engine Optimization
https://news-life.pro/moscow/402440904/
Placing the install on worth custody sites
http://autoindnews.ru/PressRelease/PressReleaseShow.asp?id=778042
Placing the site on quality trust sites
https://news-life.pro/moscow/402440904/
Mailing
http://autoindnews.ru/PressRelease/PressReleaseShow.asp?id=778042
ПВХ потолки натяжные
Сто процентный отличный материал...
Лампочки в натяжной потолок Какие лучше поставить?
Оставте свою оценку!
Mountains are among the planet’s most beautiful places. They’re
Jan Beutel was half-watching a live stream of Kleines Nesthorn, a mountain peak in the Swiss Alps, when he realized its cacophony of creaks and rumbles was getting louder. He dropped his work, turned up the sound and found himself unable to look away.
кракен
“The whole screen exploded,” he said.
Beutel, a computer engineer specializing in mountain monitoring, had just witnessed a glacier collapse. On May 28, an avalanche of millions of tons of ice and rock barreled down the slope, burying Blatten, a centuries-old village nestled in the valley below.
Local authorities had already evacuated the village after parts of the mountain had crumbled onto the glacier; a 64-year old man believed to have stayed remains missing.
But no one expected an event of this magnitude.
Successive rock avalanches onto the glacier increased the pressure on the ice, causing it to melt faster and the glacier to accelerate, eventually destabilizing it and pushing it from its bed. The collapse was sudden, violent and catastrophic. “This one just left no moment to catch a breath,” Beutel said.
The underlying causes will take time to unravel. A collapse of this magnitude would have been set in motion by geological factors going back decades at least, said Matthias Huss, a glaciologist at the Swiss university ETH Zurich.
But it’s “likely climate change is involved,” he said, as warming temperatures melt the ice that holds mountains together. It’s a problem affecting mountains across the planet.
People have long been fascinated with mountains for their dramatic beauty. Some make their homes beneath them — around 1 billion live in mountain communities — others are drawn by adventure, the challenge of conquering peaks.
These majestic landscapes have always been dangerous, but as the world warms, they are becoming much more unpredictable and much deadlier.
“We do not fully understand the hazard at the moment, nor how the dangers are changing with climate change,” said David Petley, an Earth scientist at the University of Hull in England.
Натяжные потолки ПВХ
Полезный и хороший материал...
Выбираем натяжные потолки - купить в Москве!
Оставляйте свое мнение!
Pages
Add new comment